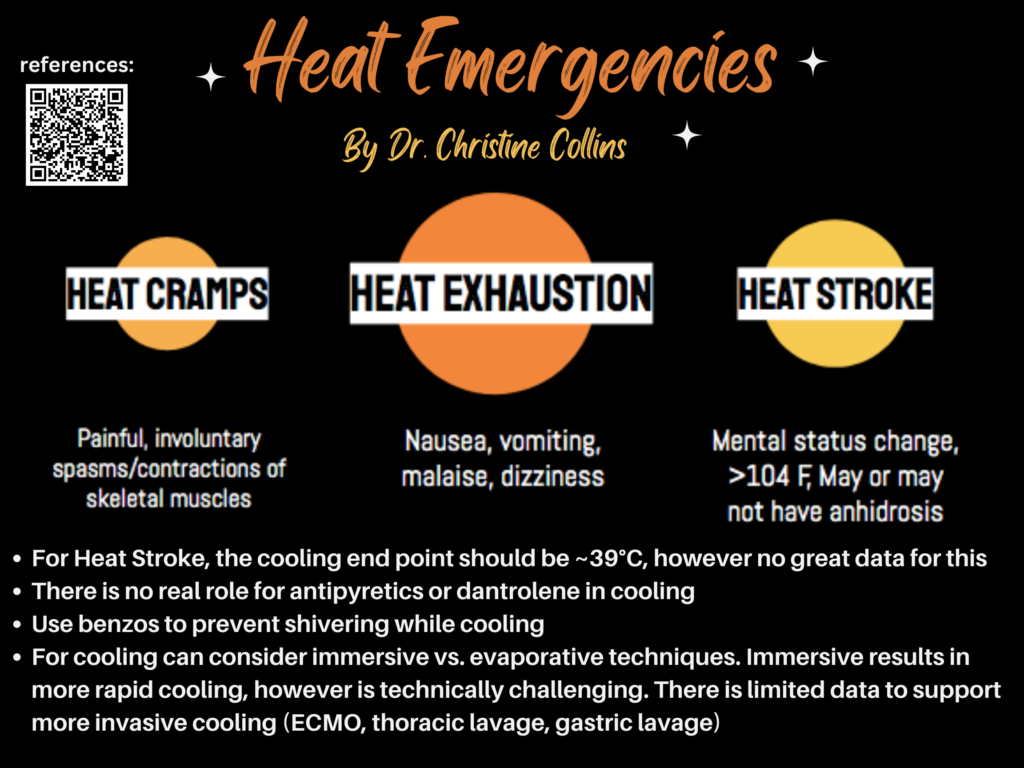
An 8-month-old female with no past medical history presents to the ED for fever. Her mother states that her child has had a fever for three days and has been otherwise acting like herself. She has been receiving acetaminophen every four hours as prescribed by her pediatrician. The last dose was given two hours ago. Vitals are: Temp 102.4, HR 150, RR 30, SpO2 99% RA. Exam shows a happy appearing child with no focal findings. A catheterized urine sample is collected which shows 2+ leukocyte esterase and 6 WBC/hpf. What is the most common causative organism of this patient’s condition?
A: E. Coli
B: Group B streptococci
C: Klebsiella pneumoniae
D: Staphylococcus aureus
E: Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Answer: A. E. Coli
The cause of this infant’s fever is most likely presenting with a urinary tract infection given her urinalysis findings. The gold standard for diagnosis of a UTI is a urinalysis with 2+ leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or > 5 WBC/hpf with bacteriuria. Urine culture should be collected in all pediatric patients with suspected UTI regardless of UA results. E. Coli is the most common cause of UTIs overall including the general pediatric population. Group B streptococci, Klebsiella, Staph aureus, and Staph saprophyticus are all much less common.
References:
Dart R.C., & White J (2020). Snakebite. Tintinalli J.E., & Ma O, & Yealy D.M., & Meckler G.D., & Stapczynski J, & Cline D.M., & Thomas S.H.(Eds.), Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 9e. McGraw Hill.
https://www.chop.edu/clinical-pathway/urinary-tract-infection-uti-febrile-clinical-pathway