A 50 year old male with a past medical history of Crohn disease with ileocolectomy presents via EMS for shortness of breath. Prior to arrival to ED, patient was found to be hypoxic and in acute respiratory distress prompting rapid sequence intubation by EMS. Vital signs are notable for hypotension and tachycardia. On exam, there are equal breath sounds bilaterally. His abdomen is distended with bruising on the left flank. GCS is 3T. A portable chest x-ray is obtained to confirm endotracheal tube placement and is shown below. What’s the diagnosis?
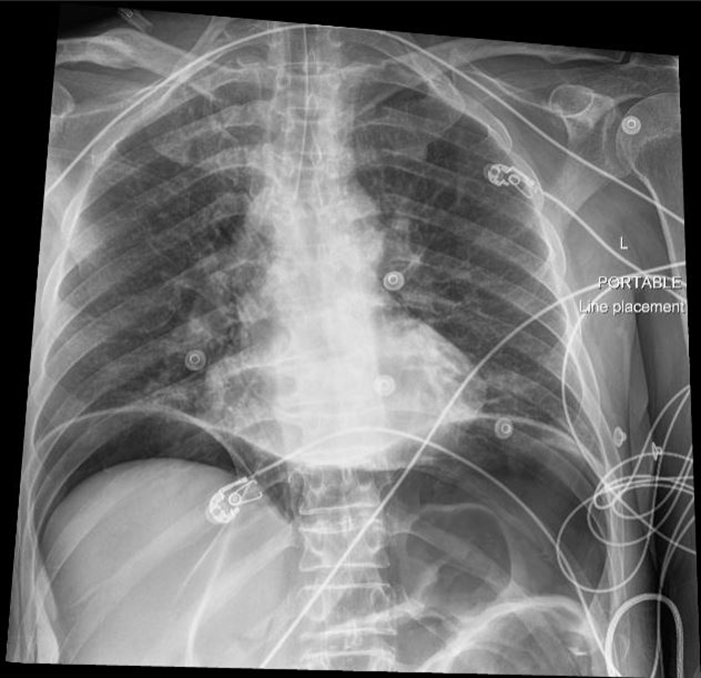
Answer: Pneumoperitoneum
- Most commonly caused by gastrointestinal perforation from etiologies such as peptic ulcer disease, traumatic injury, bowel obstruction, or infection.
- While CT is the gold standard for diagnosis, a chest x-ray may be utilized to quickly assess for presence of subdiaphragmatic air.
- Sensitivity of upright chest x-ray to detect pneumoperitoenum varies across studies but is up to 80%.
- Upright positioning for 10 minutes prior to radiograph or lateral upright positioning may increase sensitivity to over 90%.
- Specificity is approximately 90%.
- Management includes emergent surgical consultation, broad spectrum antibiotics with anaerobic coverage, and gastric decompression.
References:
Bogle AM, Gratton MC. Peptic Ulcer Disease and Gastritis. In: Tintinalli JE, Ma O, Yealy DM, Meckler GD, Stapczynski J, Cline DM, Thomas SH. eds. Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 9e. McGraw-Hill Education; 2020.
Stapakis JC, Thickman D. Diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum: abdominal CT vs. upright chest film. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1992;16:713–16.
Woodring JH, Heiser MJ. Detection of pneumoperitoneum on chest radiographs: comparison of upright lateral and posteroanterior projections. Am J Roentgenol 1995;165:45–7.